Introduction
Every vessel, from the smallest recreational craft to vast ocean-going ships, relies on a well-designed marine exhaust system to ensure safe and efficient engine operation. These complex systems are engineered to protect both vital engine components and the people aboard, while also playing a crucial role in adhering to increasingly stringent global emissions standards. Marine exhaust systems are tasked not only with removing toxic and hot gases but also with dampening noise, preventing water intrusion, and minimizing the boat’s environmental impact.
A thorough understanding of the core functions and interplay of each exhaust component is essential for seamanship, making routine inspections and ongoing maintenance a fundamental aspect of marine safety. Suppose you wish to learn more about related subsystems or need replacement parts. In that case, you can browse a comprehensive selection of marine engine room parts to keep your vessel dependable and seaworthy. Now, let’s break down the critical purpose of every major marine exhaust system part, along with why attentive care keeps your vessel ready for anything.
Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is essentially the “gateway” where exhaust gases begin their path out of the engine. As the first component to handle the intense heat and volume of gases expelled from the combustion process, it is constructed from robust steel or specially treated cast iron to withstand constant thermal cycling and exposure to saltwater. Over time, even the toughest manifolds are exposed to condensation, corrosive fumes, and physical stresses from engine vibration or shifting loads at sea.
A compromised manifold can be catastrophic, causing exhaust and seawater leaks that can corrode engine parts, damage electronics, or even pose a threat to the crew’s safety through exposure to toxic fumes. Early signs of trouble include visible rust, audible leaking sounds, or a persistent exhaust odor below decks. Routine, careful inspections—supported by timely replacement of gaskets or studs—preserve the manifold’s structural integrity and prolong system life. Dive deeper into function and maintenance tips at this exhaust manifold guide. Even minor cracks or loose fittings can escalate quickly under high operating pressures and temperatures. Addressing these minor issues early can prevent costly downtime and ensure safe vessel operation.
Exhaust Risers
Exhaust risers transport hot exhaust gases up and over the vessel’s waterline, forming a crucial “trap” against water backflow. Properly designed risers have internal cooling channels—usually cooled by pumped seawater—to ensure that surface temperatures don’t ignite surrounding materials or cause burns upon accidental contact. Poorly maintained risers, or those affected by corrosion or internal carbon deposits, can restrict gas flow and increase engine room temperatures, thereby elevating the risk of overheating.
If seawater is permitted to flow backward into the engine, it can irreparably damage cylinders and pistons. Inspection for exterior rust, deterioration at joints, or strange exhaust noises can highlight early issues. Ensure that risers are always clear, securely mounted, and leak-free to guarantee reliable operation, even in rough seas.
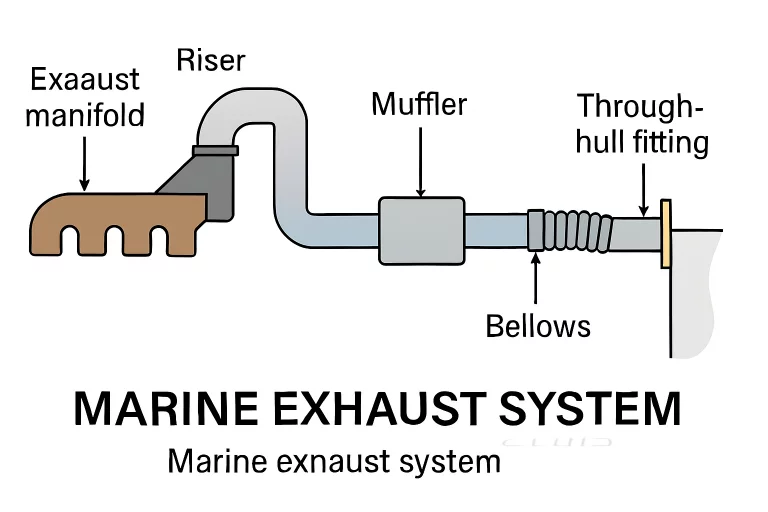
Mufflers
Marine mufflers, sometimes referred to as silencers, serve the dual role of minimizing noise pollution and dampening harmful pressure pulses in the exhaust stream. They achieve this using a series of sound-deadening chambers and baffles designed to disrupt, absorb, and dissipate the violent bursts of noise that occur as exhaust exits the engine.
Selecting the right muffler depends on the vessel’s size, engine output, and the owner’s expectations regarding onboard noise. Larger ships might employ labyrinthine or water-injection mufflers, while smaller craft typically use compact, straight-through types. Regular checks for signs of corrosion, intake blockages, or any evidence of water inside the muffler help prevent costly or hazardous failures during operation, preserving the calm and comfort of life at sea.
Water-Cooled Exhaust Pipes
Managing extreme heat is a significant challenge for any marine engine room, where water-cooled exhaust piping plays a crucial role. These pipes introduce seawater into the system as a cooling agent, rapidly dropping exhaust gas temperatures and preventing pipe surfaces from overheating. This process protects both sensitive equipment and structural materials such as fiberglass or wood, lowering the risk of thermal damage and accidental fires.
Mineral deposits from seawater, coupled with general wear and tear from vibration, can degrade these pipes and their connections over time. Frequent inspections are critical—look for evidence of drips, mineral scaling, or hose deterioration, as even a small leak can escalate quickly into a significant hazard. Maintaining leak-free water-cooled exhaust pipes is fundamental for both safety and engine longevity.
Through-Hull Fittings
The exhaust system’s safe exit point is the through-hull fitting. This marine-grade sealed port allows hot gases and expelled seawater to exit beneath or beside the waterline, away from vulnerable deck areas. These fittings must create a watertight barrier, as poorly installed or corroded outlets are a primary cause of flooding or swamping in heavy weather.
Use only corrosion-resistant materials such as bronze or high-quality stainless steel, reinforced with marine-specific sealing compounds for optimal durability. Periodically check that fittings are clear of debris, fastened securely, and that rubber gaskets or backing plates have not come loose. Proactive upkeep ensures your vessel’s final exhaust outlet remains safe, secure, and trouble-free.
Exhaust Bellows
Elasticity is vital in marine exhaust lines, which is why exhaust bellows—flexible connectors made of vulcanized rubber or corrugated stainless steel—are included at key stress points. Bellows absorb mechanical engine movement, compensate for hull flexing, and allow for modest pipe shifts due to thermal expansion during operation.
Over time, exposure to heat, salt, and vibration can compromise the bellows’ integrity, leading to pinholes, cracks, or even complete ruptures. During every maintenance cycle, check for softness, splitting, or bulging. A failing bellows can leak both toxic gases and seawater, posing a threat to interior spaces and nearby electronics.
Scrubber Systems
In recent years, exhaust gas scrubber systems have become increasingly crucial for larger vessels, particularly those navigating international waters that are subject to strict emissions regulations. These advanced systems filter and chemically “scrub” SOx and particulate matter from exhaust streams, usually by washing them with water and trapping harmful byproducts in specialized tanks.
Operating and maintaining scrubbers involves much more than simply monitoring fluid levels. Filters require periodic replacement, calibration must be regularly verified, and all captured residues must be disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations. These systems are not only essential for meeting current maritime compliance requirements but also for granting vessels unrestricted access to protected waterways and emission-controlled ports. Learn more in this overview: marine exhaust gas systems guide. Neglecting these maintenance tasks can lead to reduced system efficiency, costly repairs, or even regulatory penalties. Ensuring proper operation not only protects the environment but also safeguards the vessel’s operational reliability and reputation.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
The seamless function of the exhaust system is fundamental to safe seafaring. Proactive maintenance includes inspecting each section for loose clamps, leaks, corrosion, or buildup, ensuring that potential hazards are caught and corrected before they compromise the vessel or the environment. The cost and effort of regular preventative checks are far outweighed by the expense and danger of catastrophic failures at sea.
Always follow the guidelines provided by your engine and exhaust manufacturer for service frequency and parts replacement. Well-documented maintenance not only enhances the reliability and longevity of your vessel but also serves as proof of compliance with safety and pollution standards. This attention to detail delivers peace of mind, minimizes downtime, and ensures passenger comfort by reducing noise, fumes, and risk throughout your voyage.















